 The crescent sign of ruptured baker's cyst - Mizumoto - 2019 - Journal of General and Family Medicine - Wiley Online Library
The crescent sign of ruptured baker's cyst - Mizumoto - 2019 - Journal of General and Family Medicine - Wiley Online LibraryBaker's cyst Other multiplier cyst names Ultrasound image of Baker's cyst symptomsNo is, swelling behind the knee, stiffness, pain, , , habitual introduction Knee problems such as , , Confirmed by or , , Treatment, surgeryFrequencyc. 20% Baker's cyst, also known as popliteal cyst, is a type of fluid collection behind it. Often there are no symptoms. If symptoms occur, they may include swelling and pain behind the knee, or stiffness of the knee. If the cyst opens, the pain can increase significantly with calf swelling. Rare complications such as , , , or may occur. Baker's cystpopliteal cyst Risk factors include other knee problems such as , , or . The underlying mechanism involves the flow of the to , leading to its expansion. Diagnosis can be confirmed with or (RM). Treatment is initially with . If this is not effective, injection or surgical removal can be performed. About 20% of people have a Baker cyst. They occur more commonly in those 35 to 70 years old. He is appointed by the surgeon who first described him, (1838-1896). Content Signs and symptoms[ ] Symptoms may include swelling behind the knee, stiffness and pain. If the cyst opens, the pain may increase and there may be swelling of the calf. The cyst of a baker can also cause under the ankle (sort of residue). Case[] In adults, Baker cysts usually arise from almost any form of knee (e.g., ) or (e.g. one ) tear. Baker's cysts in children do not point to the underlying joint disease. Baker cysts arise between the tendons of the middle head of the and the . They are after the . The sac of the joint of the knee can, under certain circumstances, produce a posterior lump, in the , the space behind the knee. When this lump is made big enough, it becomes palpable and cystic. Most of Baker's cysts keep this direct communication with the cavity of the knee, but sometimes the new cyst is clear. The cyst of a baker can break and produce acute pain behind the knee and in the calf and swelling of the . Diagnosis[] Diagnosis is by test. The cyst of a baker is easier to see from the back with the patient standing with the knees fully extended. It is easier to palp (felt) with the knee partially flexed. The diagnosis is confirmed by , although if necessary and there is no suspicion of a synovial fluid aspiration of the cyst can be performed carefully. An image can reveal the presence of Baker's cyst. An infrequent but life-threatening complication, which may need to be excluded by blood and ultrasound analysis, is a (DVT). It is possible that a rapid evaluation of the possibility of DVT is required when Baker's cyst has compressed vascular structures, causing edema of the leg, as it establishes conditions for a DVT to develop. A burst cyst commonly causes calf pain, swelling, and redness that can be imitated. A copy of a body from Baker's cyst in popliteal space Baker's cyst in the axial MRI with communicative channel between the semi-membranous muscle and the medial head of the gastrocnemium muscle. Baker's cyst in MRI, sagittal image Baker's cyst in MRI, sagittal image Treatment[] Baker cysts usually do not require treatment unless they are. It is very rare that the symptoms are coming out of the cyst. In most cases, there is another disorder in the knee (arthritis, meniscal tear (cartilage), etc.) that is causing the problem. The initial treatment should be directed to correct the source of increased fluid production. Often rest and leg lifting are all you need. If necessary, cyst may be to reduce its size, then injected with one to reduce inflammation. is reserved for cysts that cause a lot of discomfort to the patient. A broken cyst is treated with rest, leg elevation and injection of a corticosteroid on the knee. Baker's cysts in children, unlike older people, almost always disappear over time, and rarely require excision. [] Sometimes it can be an effective way to control Baker's cyst-related pain.[] Heat is also commonly used.[] A knee can provide support to give the feeling of stability in the joint. [] Exercise[] Many activities can put tension on the knee, and cause pain in the case of Baker's cyst. Avoiding activities such as escape, kneeling, heavy lifting, climbing, and even running can help prevent pain. Despite this, some exercises can help relieve pain, and one can instruct on stretching and strengthening the and/or .[] References[]abcdefghijklmn45abcdefabcdefgh37abcdExternal links[] ############## Non-capsular BoardsSymptoms //.mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal}upper limb lower another/general: Nonjoint / Symptoms //.mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal}upper limb lower another/general: .mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal}upper limb lower another/general: / Navigation menu Personal tools Named spaces Variants Views More Search Navigation Contributed Tools Printing/exporting Other projects Languages
Original contribution Cyst-multiplier and pseudotromboflebitis syndrome Fifteen patients presented during a four-year period with pseudotromboflebitis syndrome, later confirmed arthrographically as a result of the rupture of the popliteal cyst. Initially, the majority of patients (73%) were misdiagnosed with calf vein thrombosis, and were anticoagulated for periods of three to ten days. The clinical differentiation of venous thrombosis was generally impossible. Contrast arthrography was definitive diagnostic research, revealing popliteal cysts in all patients, and an active synovial escape in the calf in 13 cases (87%). The average delay in performing the arthrography was 5.3 days, the procedure is usually performed after the normal contrast venography. Doppler's venography and isotope produced deceptive or deceptive results (42%) delaying the misdiagnosis and prolonging periods of potentially dangerous anticoagulation. We suggest that the superposition marked in the emergency presentation of popliteal cyst rupture and calf vein thrombosis entrusts the aggressive use of arthrography combined with venography in all patients who have a painful swollen leg. Recommended articles Cite articles Metrics of the article We use cookies to help provide and improve our service and personalized content and ads. By continuing to accept . Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or collaborators. Direct Science ® is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V.ScienceDirect ® is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V.

Popliteal Ecchymosis in Ruptured Baker's Cyst - The American Journal of Medicine
Image of the Week: A fisherman presents with bruising - Clinical Advisor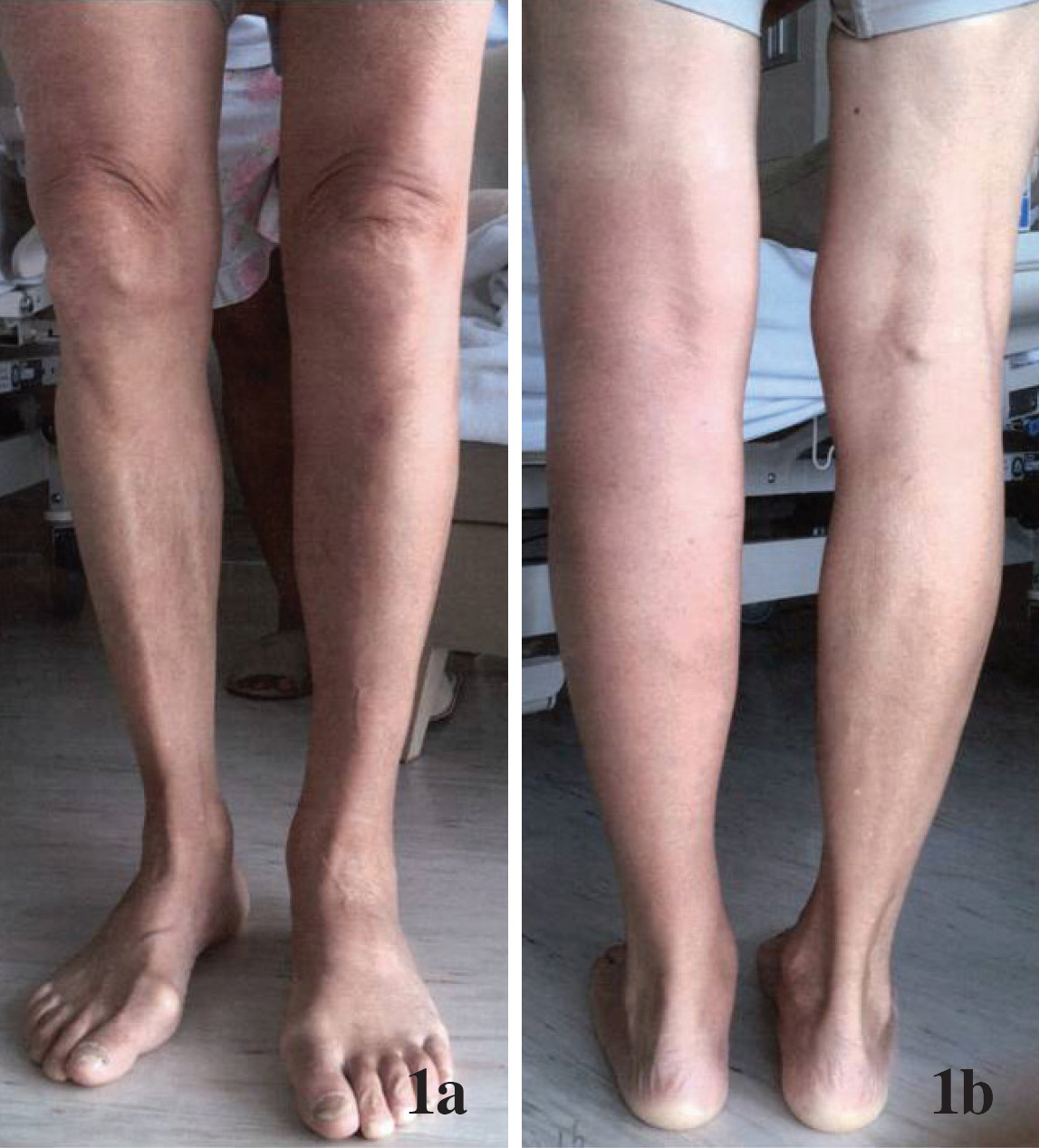
Differentiation between ruptured Baker's cyst and deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Baker Cysts – It's the little things that matter
The Hemorrhagic Crescent Sign of Acute Synovial Rupture
Ruptured popliteal cyst diagnosed by ultrasound before evaluation for deep vein thrombosis. - Abstract - Europe PMC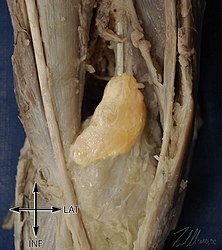
Baker's cyst - Wikipedia
Unilateral calf swelling - European Journal of Internal Medicine
Baker's Cyst. What is it and how is it treated? – Mending, Coaching & Inspiring Athletes.
Baker's Cyst - PT Master Guide
PDF) A man with swollen calf and discoloration of the foot - Ruptured Baker's cyst.
The crescent sign of ruptured baker's cyst - Mizumoto - 2019 - Journal of General and Family Medicine - Wiley Online Library
Baker's cyst - Health&
Differentiation between ruptured Baker's cyst and deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
A lateral view showing the swollen and erythematous left calf. | Download Scientific Diagram![USMLE Step 2 CK対策bot on Twitter:]()
USMLE Step 2 CK対策bot on Twitter: "Crescent sign Baker cystの破裂に特徴的 https://t.co/LJV1gYykhJ"
Baker's Cyst - Symptoms, Diagnois and Treatment Options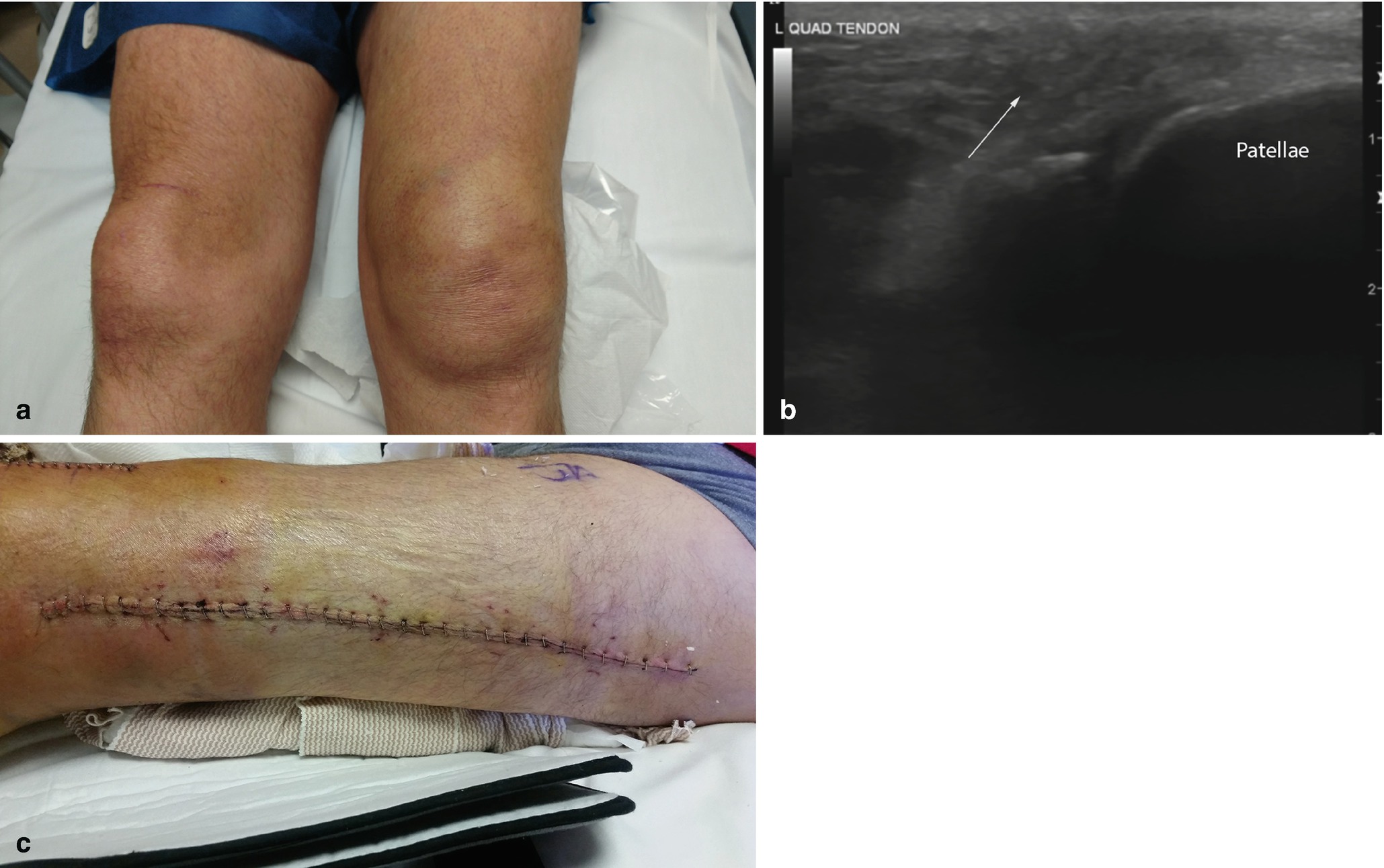
Complications | SpringerLink
Rheumatoid Arthritis. - ppt download
Homans Sign - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Figure 28 from Ecchymosis of the lower leg. A sign of hemarthrosis with synovial rupture. | Semantic Scholar
Popliteal Vein - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Figure 1 from Ecchymosis of the lower leg. A sign of hemarthrosis with synovial rupture. | Semantic Scholar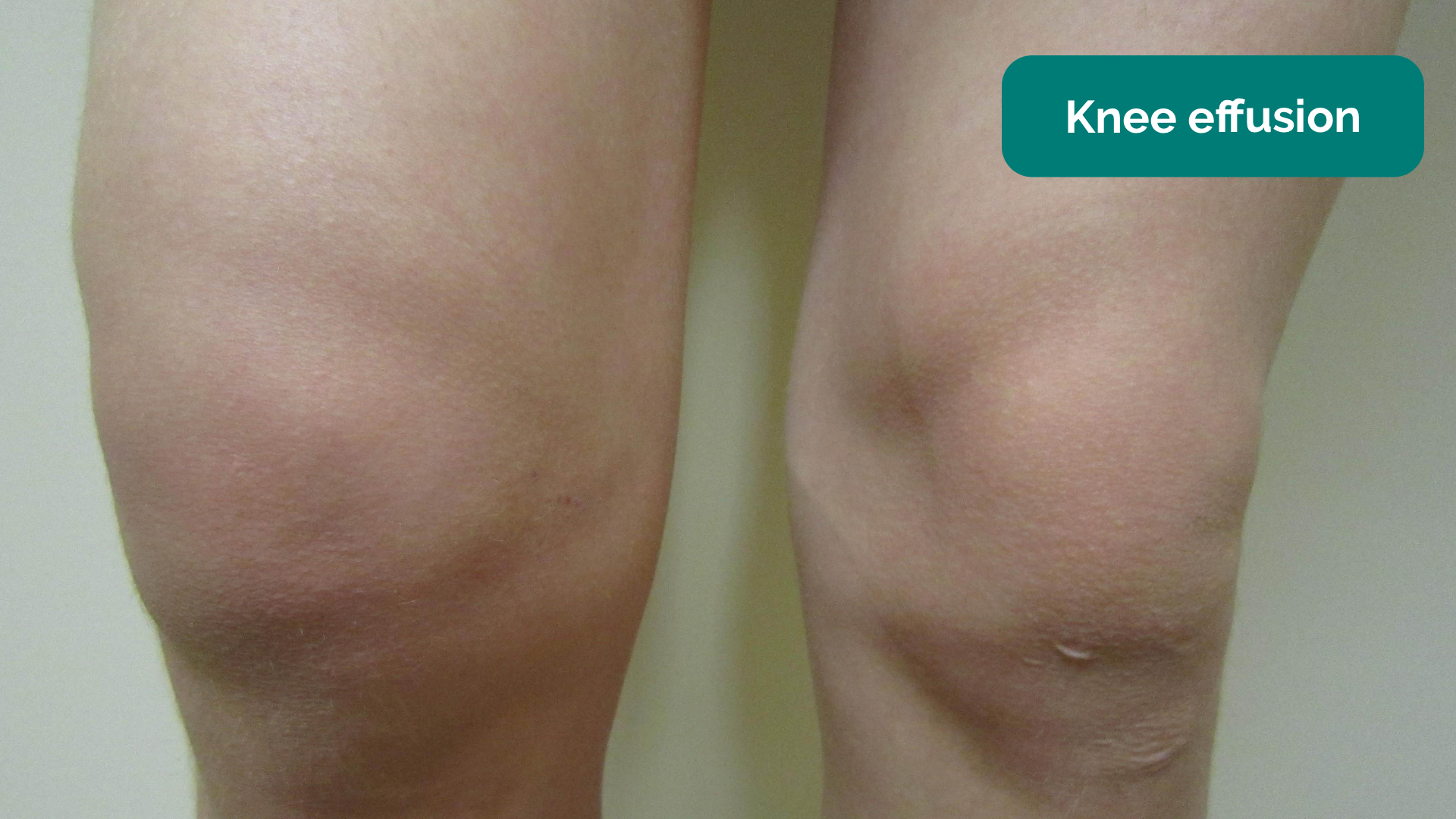
Knee Examination - OSCE Guide | Geeky Medics
Infected Baker's Cyst: A New Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment Recommendations | Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports
Differentiation between ruptured Baker's cyst and deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Baker's cyst - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic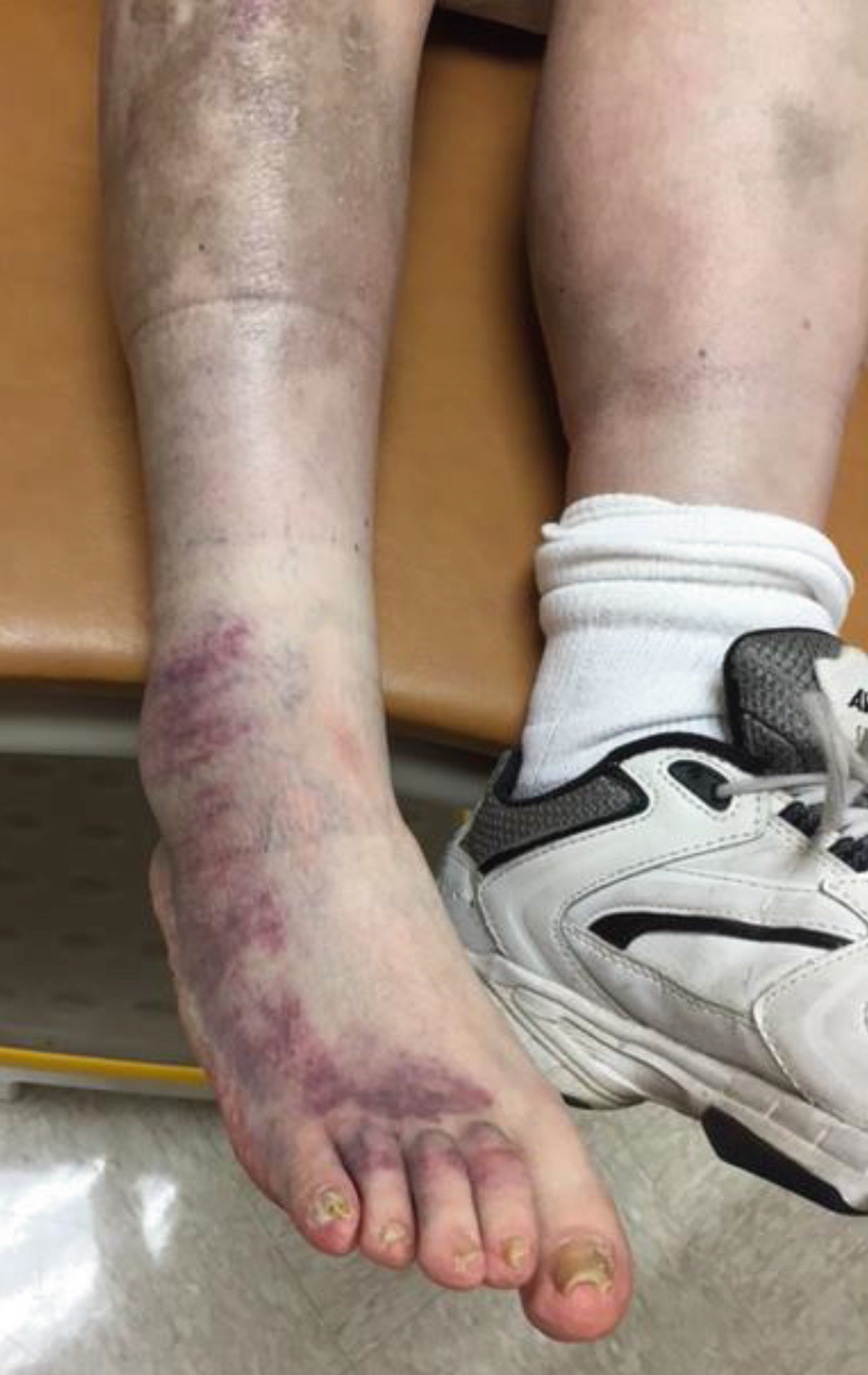
Questions 31–40 | SpringerLink
Ruptured Baker's Cyst: Treating a Ruptured Popliteal Cyst
A man with swollen calf and discoloration of the foot | Postgraduate Medical Journal
MSK Final Exam: Dr. Finley (Nic Tan) Flashcards | Quizlet
Baker's Cyst — A Common Type of Knee Pain | Everyday Health
Knee Examination - OSCE Guide | Geeky Medics
Baker's cyst - Wikipedia
Orthopedic Causes of Edema - ppt download
Knee – Baker's Cyst of the Knee | AOA Orthopedic Specialists
The swollen leg
Baker's Cyst Pictures (Page 1) - Line.17QQ.com
Infected Baker's Cyst: A New Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment Recommendations
The swollen leg
 The crescent sign of ruptured baker's cyst - Mizumoto - 2019 - Journal of General and Family Medicine - Wiley Online Library
The crescent sign of ruptured baker's cyst - Mizumoto - 2019 - Journal of General and Family Medicine - Wiley Online Library






























Posting Komentar untuk "baker cyst crescent sign"